Circuit Boards 101

What is a Circuit Board?
A circuit board, also known as printed circuit board or PCB, can be found inside every electronic device in today’s world. In fact, the circuit board is considered the foundation of electronic devices because it is where the individual components are held in place and interconnected to make the electronic device work as intended.
.jpg?lang=en-US)
Picture: Circuit board with green Solder Mask, without components (bare).
In its simplest form, a circuit board is a non-conductive material with conductive tracks made of metal (usually copper) to physically support and electrically interconnect the components needed for an electronic device.
A design engineer working on a specific electronic device will create a custom pattern of electrically conductive tracks (called traces) with features like pads and holes where the components will be mounted onto and interconnected. Since different devices require different components and interconnection to achieve the intended functionality, the pattern of copper tracks and conductive features on the substrate will vary from one circuit board design to another.
More complex circuit boards will have many layers of conductive copper tracks and interconnecting features sandwiched between non-conductive material. With technology advancing and the demand for electronic devices to become smaller with increased functionality rising,engineers are pushing the boundaries of design and manufacturing capabilities to create circuit boards with finer features, higher numbers of conductive layers, and smaller and more densely packed components. These advanced circuit boards are often referred to as HDI or high density interconnect PCBs. To learn more about HDI PCBs, click here.
What Are Circuit Boards Made Of?
The most common non-conductive material used to support the etched copper tracks and conductive features in a circuit board is a composite material made of woven fiberglass cloth and epoxy resin. Surprisingly, this material is usually an off-white color, not green. The green color (or any other color) is added later as one of the final steps in the circuit board manufacturing process. This added layer of color is called Solder Mark and is used to protect the top and bottom layers of copper which would otherwise be exposed.
Although the common substrate made of fiberglass and epoxy resin is adequate for many electronic devices, it may not be for others since not all devices are made for the same purpose, application, or environment. Many electronic devices require that the PCB substrate meet certain properties, and therefore, demand a more advanced or specialized type of substrate. These requirements can include a certain level of temperature resistance, shock resistance, and brittleness just to name a few, but the list of properties and qualifications can be extensive. Click the link to learn more about the different types of materials available for circuit board manufacturing.
Manufacturing Circuit Boards
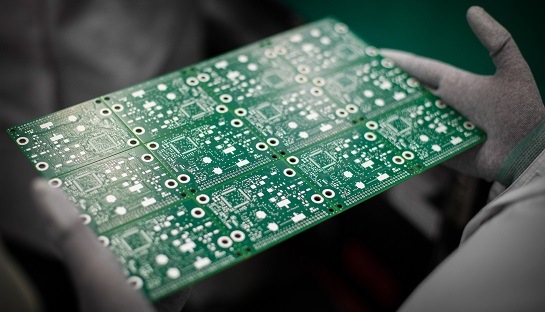
Picture: Bare circuit board array with 0 and 90 degree score lines.
As PCB fabrication technology evolves, it has become cheaper, faster, and more convenient to have printed circuit boards professionally fabricated. Most PCB manufactures require Gerber files to manufacture circuit boards, which contain the data, drawings, and specifications for a particular circuit board design to be produced.
PCB design automation software such as AdvancedPCB’s PCB Artist® enables design engineers to layout their circuit board design according to their needs and requirements to later export that data for their circuit board manufacturer. The manufacturer uses the electronic data and fabrication drawings to set up automated equipment to produce the circuit boards with matching specifications and features.
Click the links below to learn more about printed circuit boards & PCB manufacturing:

AdvancedPCB
Related Posts

Future trends of the circuit board

2-Layer vs. 4-Layer Printed Circuit Boards



